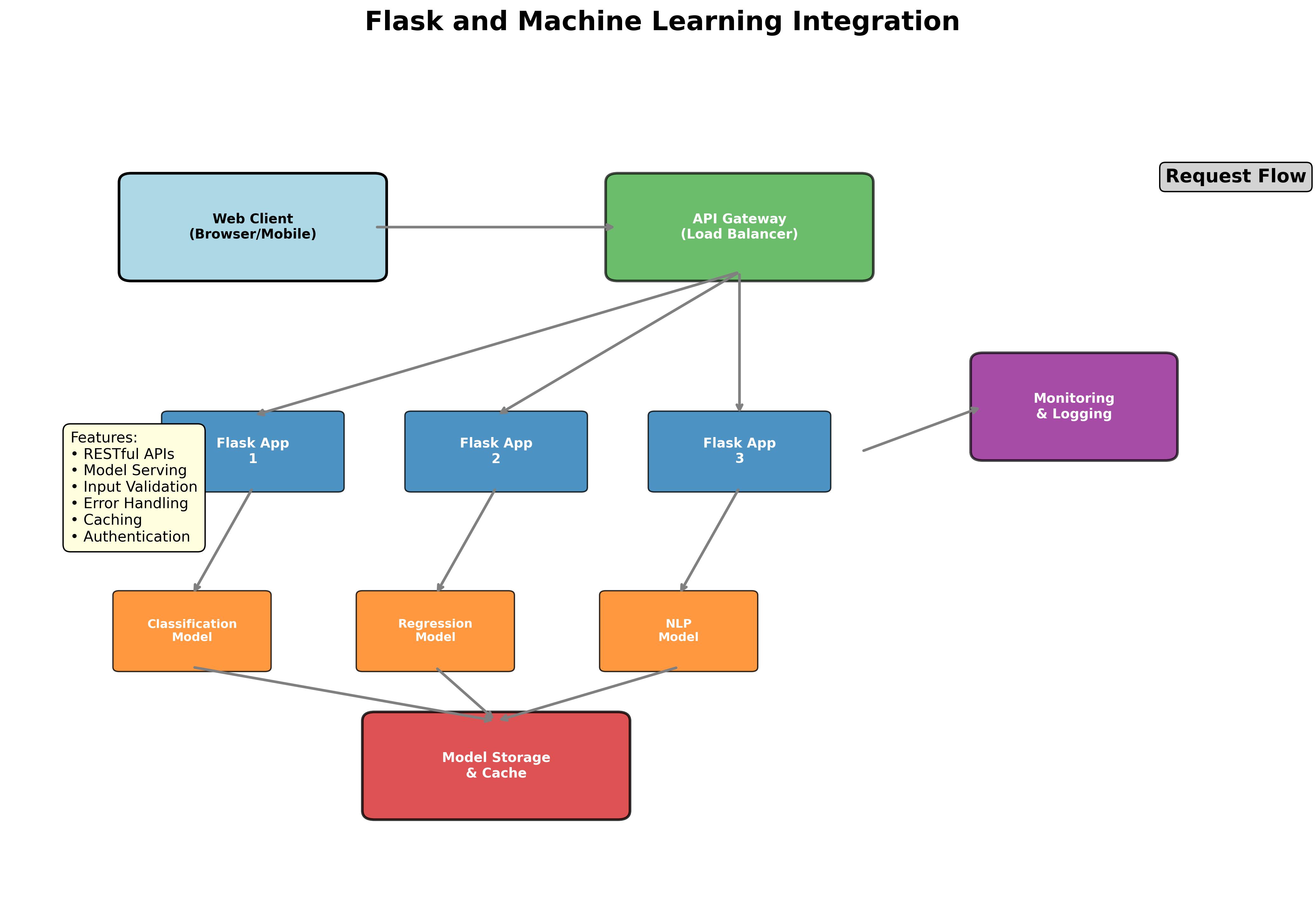
Flask and Machine Learning Integration: Building Production-Ready ML APIs
updatedAt: "2025-01-28T14:00:00Z" featured: true type: "text" views: 892 videoUrl: "" watchTime: ""
Flask and Machine Learning Integration: Building Production-Ready ML APIs
Flask, Python's lightweight web framework, provides an excellent foundation for deploying machine learning models as web services. This comprehensive guide will walk you through integrating ML models with Flask, from basic setups to production-ready deployments with proper error handling, validation, and scalability considerations.
 Figure 1: Flask provides a lightweight yet powerful framework for deploying machine learning models as web services.
Figure 1: Flask provides a lightweight yet powerful framework for deploying machine learning models as web services.
Table of Contents
- Why Flask for ML Deployment?
- Setting Up Your Environment
- Basic ML Model Integration
- Building RESTful ML APIs
- Model Management and Serialization
- Input Validation and Error Handling
- Real-time Predictions
- Batch Processing
- Performance Optimization
- Security Considerations
- Testing ML APIs
- Deployment Strategies
- Monitoring and Logging
- Complete Project Example
Why Flask for ML Deployment? {#why-flask}
Flask offers several advantages for machine learning deployment:
Simplicity and Flexibility
- Minimal boilerplate code
- Easy to understand and modify
- Flexible architecture for different ML use cases
Python Ecosystem Integration
- Seamless integration with scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch
- Rich ecosystem of ML libraries
- Easy model serialization with pickle, joblib
Lightweight and Fast
- Low overhead for simple ML APIs
- Quick startup times
- Efficient for microservices architecture
Extensibility
- Easy to add authentication, logging, monitoring
- Extensive plugin ecosystem
- Can scale with Flask extensions
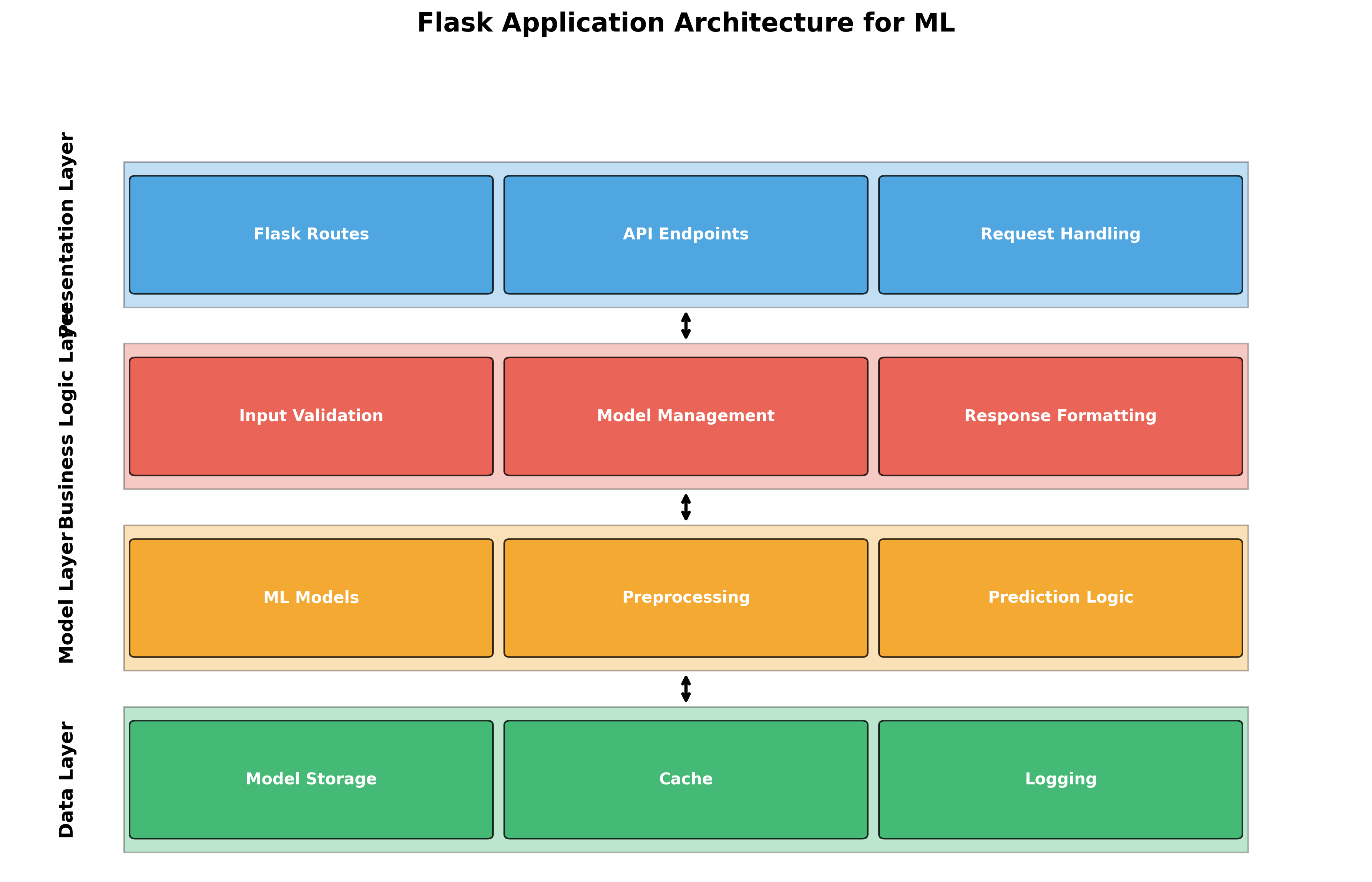 Figure 2: Flask's modular architecture makes it ideal for ML microservices.
Figure 2: Flask's modular architecture makes it ideal for ML microservices.
Setting Up Your Environment {#setup}
Let's start by setting up a proper development environment for Flask ML integration.
Project Structure
flask-ml-app/
├── app/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── models/
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── ml_models.py
│ ├── api/
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── routes.py
│ └── utils/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── validators.py
│ └── preprocessors.py
├── models/
│ ├── trained_model.pkl
│ └── scaler.pkl
├── tests/
│ ├── test_api.py
│ └── test_models.py
├── requirements.txt
├── config.py
└── run.py
Dependencies
# requirements.txt
Flask==2.3.3
Flask-RESTful==0.3.10
Flask-CORS==4.0.0
scikit-learn==1.3.0
pandas==2.0.3
numpy==1.24.3
joblib==1.3.2
marshmallow==3.20.1
gunicorn==21.2.0
pytest==7.4.0
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Basic ML Model Integration {#basic-integration}
Let's start with a simple example of integrating a trained model with Flask.
Training and Saving a Model
# train_model.py
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
import joblib
def train_model():
"""Train a simple classification model"""
# Generate sample data (replace with your dataset)
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=1000,
n_features=20,
n_informative=15,
n_redundant=5,
n_classes=3,
random_state=42
)
# Split the data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# Scale features
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
# Train model
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
# Evaluate
y_pred = model.predict(X_test_scaled)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Model Accuracy: {accuracy:.3f}")
# Save model and scaler
joblib.dump(model, 'models/trained_model.pkl')
joblib.dump(scaler, 'models/scaler.pkl')
print("Model and scaler saved successfully!")
return model, scaler
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_model()
Basic Flask Application
# app/__init__.py
from flask import Flask
from flask_cors import CORS
def create_app():
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app) # Enable CORS for API access
# Register blueprints
from app.api.routes import api_bp
app.register_blueprint(api_bp, url_prefix='/api')
return app
# app/models/ml_models.py
import joblib
import numpy as np
import os
from typing import Optional, Dict, Any
class MLModelManager:
"""Manages loading and predictions for ML models"""
def __init__(self):
self.model = None
self.scaler = None
self.model_loaded = False
def load_model(self, model_path: str = 'models/trained_model.pkl',
scaler_path: str = 'models/scaler.pkl'):
"""Load the trained model and scaler"""
try:
if os.path.exists(model_path) and os.path.exists(scaler_path):
self.model = joblib.load(model_path)
self.scaler = joblib.load(scaler_path)
self.model_loaded = True
print("Model and scaler loaded successfully!")
else:
raise FileNotFoundError("Model or scaler file not found")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading model: {str(e)}")
self.model_loaded = False
def predict(self, features: np.ndarray) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Make prediction with confidence scores"""
if not self.model_loaded:
raise ValueError("Model not loaded. Call load_model() first.")
try:
# Scale features
features_scaled = self.scaler.transform(features.reshape(1, -1))
# Get prediction and probabilities
prediction = self.model.predict(features_scaled)[0]
probabilities = self.model.predict_proba(features_scaled)[0]
# Get class names (assuming classes are 0, 1, 2)
classes = self.model.classes_
return {
'prediction': int(prediction),
'confidence': float(max(probabilities)),
'probabilities': {
f'class_{classes[i]}': float(prob)
for i, prob in enumerate(probabilities)
}
}
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(f"Prediction error: {str(e)}")
def batch_predict(self, features_batch: np.ndarray) -> list:
"""Make predictions for multiple samples"""
if not self.model_loaded:
raise ValueError("Model not loaded. Call load_model() first.")
try:
# Scale features
features_scaled = self.scaler.transform(features_batch)
# Get predictions and probabilities
predictions = self.model.predict(features_scaled)
probabilities = self.model.predict_proba(features_scaled)
results = []
for i, (pred, probs) in enumerate(zip(predictions, probabilities)):
results.append({
'sample_id': i,
'prediction': int(pred),
'confidence': float(max(probs)),
'probabilities': {
f'class_{self.model.classes_[j]}': float(prob)
for j, prob in enumerate(probs)
}
})
return results
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(f"Batch prediction error: {str(e)}")
# Global model manager instance
model_manager = MLModelManager()
Building RESTful ML APIs {#rest-apis}
Now let's create RESTful endpoints for our ML model.
Input Validation
# app/utils/validators.py
from marshmallow import Schema, fields, validate, ValidationError
import numpy as np
class PredictionSchema(Schema):
"""Schema for single prediction request"""
features = fields.List(
fields.Float(required=True),
required=True,
validate=validate.Length(equal=20) # Expecting 20 features
)
class BatchPredictionSchema(Schema):
"""Schema for batch prediction request"""
samples = fields.List(
fields.List(
fields.Float(required=True),
validate=validate.Length(equal=20)
),
required=True,
validate=validate.Length(min=1, max=100) # Limit batch size
)
def validate_prediction_input(data):
"""Validate single prediction input"""
schema = PredictionSchema()
try:
result = schema.load(data)
return True, result, None
except ValidationError as err:
return False, None, err.messages
def validate_batch_input(data):
"""Validate batch prediction input"""
schema = BatchPredictionSchema()
try:
result = schema.load(data)
return True, result, None
except ValidationError as err:
return False, None, err.messages
API Routes
# app/api/routes.py
from flask import Blueprint, request, jsonify
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
from app.utils.validators import validate_prediction_input, validate_batch_input
import numpy as np
import time
api_bp = Blueprint('api', __name__)
@api_bp.route('/health', methods=['GET'])
def health_check():
"""Health check endpoint"""
return jsonify({
'status': 'healthy',
'model_loaded': model_manager.model_loaded,
'timestamp': time.time()
})
@api_bp.route('/predict', methods=['POST'])
def predict():
"""Single prediction endpoint"""
try:
# Get JSON data
data = request.get_json()
if not data:
return jsonify({'error': 'No JSON data provided'}), 400
# Validate input
is_valid, validated_data, errors = validate_prediction_input(data)
if not is_valid:
return jsonify({'error': 'Validation failed', 'details': errors}), 400
# Convert to numpy array
features = np.array(validated_data['features'])
# Make prediction
result = model_manager.predict(features)
return jsonify({
'success': True,
'result': result,
'timestamp': time.time()
})
except ValueError as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 400
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': 'Internal server error'}), 500
@api_bp.route('/predict/batch', methods=['POST'])
def batch_predict():
"""Batch prediction endpoint"""
try:
# Get JSON data
data = request.get_json()
if not data:
return jsonify({'error': 'No JSON data provided'}), 400
# Validate input
is_valid, validated_data, errors = validate_batch_input(data)
if not is_valid:
return jsonify({'error': 'Validation failed', 'details': errors}), 400
# Convert to numpy array
features_batch = np.array(validated_data['samples'])
# Make batch prediction
results = model_manager.batch_predict(features_batch)
return jsonify({
'success': True,
'results': results,
'count': len(results),
'timestamp': time.time()
})
except ValueError as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 400
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': 'Internal server error'}), 500
@api_bp.route('/model/info', methods=['GET'])
def model_info():
"""Get model information"""
if not model_manager.model_loaded:
return jsonify({'error': 'Model not loaded'}), 503
try:
info = {
'model_type': type(model_manager.model).__name__,
'n_features': model_manager.model.n_features_,
'n_classes': len(model_manager.model.classes_),
'classes': model_manager.model.classes_.tolist(),
'feature_importance': model_manager.model.feature_importances_.tolist()
}
return jsonify(info)
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': 'Could not retrieve model info'}), 500
Main Application
# run.py
from app import create_app
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
app = create_app()
# Load model on startup
model_manager.load_model()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True, host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
 Figure 3: RESTful API endpoints for machine learning model serving.
Figure 3: RESTful API endpoints for machine learning model serving.
Model Management and Serialization {#model-management}
Advanced Model Manager
# app/models/advanced_ml_models.py
import joblib
import pickle
import json
import os
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional
import hashlib
class AdvancedMLModelManager:
"""Advanced model manager with versioning and metadata"""
def __init__(self, models_dir: str = 'models'):
self.models_dir = models_dir
self.current_model = None
self.current_scaler = None
self.model_metadata = {}
self.model_loaded = False
def save_model(self, model, scaler, metadata: Dict[str, Any]):
"""Save model with metadata and versioning"""
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
version = metadata.get('version', timestamp)
# Create model directory
model_dir = os.path.join(self.models_dir, f"model_{version}")
os.makedirs(model_dir, exist_ok=True)
# Save model and scaler
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'model.pkl')
scaler_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'scaler.pkl')
metadata_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'metadata.json')
joblib.dump(model, model_path)
joblib.dump(scaler, scaler_path)
# Add system metadata
full_metadata = {
**metadata,
'saved_at': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'model_path': model_path,
'scaler_path': scaler_path,
'model_hash': self._calculate_hash(model_path),
'scaler_hash': self._calculate_hash(scaler_path)
}
with open(metadata_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(full_metadata, f, indent=2)
print(f"Model saved with version: {version}")
return version
def load_model(self, version: Optional[str] = None):
"""Load model by version (latest if not specified)"""
if version is None:
version = self._get_latest_version()
if version is None:
raise FileNotFoundError("No models found")
model_dir = os.path.join(self.models_dir, f"model_{version}")
if not os.path.exists(model_dir):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Model version {version} not found")
# Load metadata
metadata_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'metadata.json')
with open(metadata_path, 'r') as f:
self.model_metadata = json.load(f)
# Load model and scaler
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'model.pkl')
scaler_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'scaler.pkl')
self.current_model = joblib.load(model_path)
self.current_scaler = joblib.load(scaler_path)
self.model_loaded = True
print(f"Model version {version} loaded successfully!")
return version
def _get_latest_version(self):
"""Get the latest model version"""
if not os.path.exists(self.models_dir):
return None
model_dirs = [d for d in os.listdir(self.models_dir)
if d.startswith('model_') and
os.path.isdir(os.path.join(self.models_dir, d))]
if not model_dirs:
return None
# Sort by creation time
model_dirs.sort(key=lambda x: os.path.getctime(
os.path.join(self.models_dir, x)
), reverse=True)
return model_dirs[0].replace('model_', '')
def _calculate_hash(self, file_path: str) -> str:
"""Calculate file hash for integrity checking"""
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
return hashlib.md5(f.read()).hexdigest()
def get_model_info(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get comprehensive model information"""
if not self.model_loaded:
return {'error': 'No model loaded'}
return {
'metadata': self.model_metadata,
'model_type': type(self.current_model).__name__,
'model_params': self.current_model.get_params(),
'feature_count': getattr(self.current_model, 'n_features_', 'Unknown'),
'classes': getattr(self.current_model, 'classes_', []).tolist() if hasattr(self.current_model, 'classes_') else []
}
Input Validation and Error Handling {#validation}
Comprehensive Validation
# app/utils/advanced_validators.py
from marshmallow import Schema, fields, validate, ValidationError, post_load
import numpy as np
from typing import Dict, Any, Tuple, List
class FeatureSchema(Schema):
"""Schema for individual features with statistical validation"""
value = fields.Float(required=True)
@post_load
def validate_range(self, data: Dict[str, Any], **kwargs):
"""Custom validation for feature ranges"""
value = data['value']
# Example: Check for reasonable ranges
if not -10 <= value <= 10:
raise ValidationError(f"Feature value {value} outside expected range [-10, 10]")
return data
class EnhancedPredictionSchema(Schema):
"""Enhanced schema with metadata and validation"""
features = fields.List(
fields.Float(required=True),
required=True,
validate=validate.Length(equal=20)
)
# Optional metadata
request_id = fields.String(missing=None)
client_id = fields.String(missing=None)
@post_load
def validate_features(self, data: Dict[str, Any], **kwargs):
"""Statistical validation of features"""
features = np.array(data['features'])
# Check for NaN or infinite values
if np.any(np.isnan(features)) or np.any(np.isinf(features)):
raise ValidationError("Features contain NaN or infinite values")
# Check for outliers (simple z-score based)
z_scores = np.abs((features - np.mean(features)) / np.std(features))
if np.any(z_scores > 5): # 5 standard deviations
raise ValidationError("Features contain extreme outliers")
return data
class ErrorHandler:
"""Centralized error handling"""
@staticmethod
def handle_validation_error(error: ValidationError) -> Tuple[Dict[str, Any], int]:
"""Handle validation errors"""
return {
'error': 'Validation failed',
'details': error.messages,
'error_type': 'validation_error'
}, 400
@staticmethod
def handle_model_error(error: Exception) -> Tuple[Dict[str, Any], int]:
"""Handle model-related errors"""
return {
'error': 'Model error',
'details': str(error),
'error_type': 'model_error'
}, 503
@staticmethod
def handle_generic_error(error: Exception) -> Tuple[Dict[str, Any], int]:
"""Handle generic errors"""
return {
'error': 'Internal server error',
'details': str(error),
'error_type': 'internal_error'
}, 500
Performance Optimization {#optimization}
Caching and Performance
# app/utils/performance.py
from functools import lru_cache
import time
import hashlib
import json
from typing import Any, Dict
import numpy as np
class PredictionCache:
"""Simple in-memory cache for predictions"""
def __init__(self, max_size: int = 1000, ttl: int = 3600):
self.cache = {}
self.max_size = max_size
self.ttl = ttl # Time to live in seconds
def _hash_features(self, features: np.ndarray) -> str:
"""Create hash for feature array"""
return hashlib.md5(features.tobytes()).hexdigest()
def get(self, features: np.ndarray) -> Any:
"""Get cached prediction"""
key = self._hash_features(features)
if key in self.cache:
cached_item = self.cache[key]
if time.time() - cached_item['timestamp'] < self.ttl:
return cached_item['result']
else:
del self.cache[key] # Remove expired item
return None
def set(self, features: np.ndarray, result: Any):
"""Cache prediction result"""
if len(self.cache) >= self.max_size:
# Remove oldest item
oldest_key = min(self.cache.keys(),
key=lambda k: self.cache[k]['timestamp'])
del self.cache[oldest_key]
key = self._hash_features(features)
self.cache[key] = {
'result': result,
'timestamp': time.time()
}
class PerformanceMonitor:
"""Monitor API performance"""
def __init__(self):
self.request_times = []
self.request_count = 0
self.error_count = 0
def record_request(self, duration: float, success: bool = True):
"""Record request metrics"""
self.request_times.append(duration)
self.request_count += 1
if not success:
self.error_count += 1
# Keep only last 1000 requests
if len(self.request_times) > 1000:
self.request_times = self.request_times[-1000:]
def get_stats(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get performance statistics"""
if not self.request_times:
return {'error': 'No requests recorded'}
return {
'total_requests': self.request_count,
'error_count': self.error_count,
'error_rate': self.error_count / self.request_count if self.request_count > 0 else 0,
'avg_response_time': np.mean(self.request_times),
'p95_response_time': np.percentile(self.request_times, 95),
'p99_response_time': np.percentile(self.request_times, 99)
}
# Global instances
prediction_cache = PredictionCache()
performance_monitor = PerformanceMonitor()
Optimized API Routes
# app/api/optimized_routes.py
from flask import Blueprint, request, jsonify
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
from app.utils.performance import prediction_cache, performance_monitor
import time
import numpy as np
optimized_api_bp = Blueprint('optimized_api', __name__)
@optimized_api_bp.route('/predict/fast', methods=['POST'])
def fast_predict():
"""Optimized prediction endpoint with caching"""
start_time = time.time()
try:
data = request.get_json()
features = np.array(data['features'])
# Check cache first
cached_result = prediction_cache.get(features)
if cached_result is not None:
duration = time.time() - start_time
performance_monitor.record_request(duration, True)
return jsonify({
'success': True,
'result': cached_result,
'cached': True,
'response_time': duration
})
# Make prediction
result = model_manager.predict(features)
# Cache result
prediction_cache.set(features, result)
duration = time.time() - start_time
performance_monitor.record_request(duration, True)
return jsonify({
'success': True,
'result': result,
'cached': False,
'response_time': duration
})
except Exception as e:
duration = time.time() - start_time
performance_monitor.record_request(duration, False)
return jsonify({
'error': str(e),
'response_time': duration
}), 500
@optimized_api_bp.route('/stats', methods=['GET'])
def get_stats():
"""Get API performance statistics"""
return jsonify(performance_monitor.get_stats())
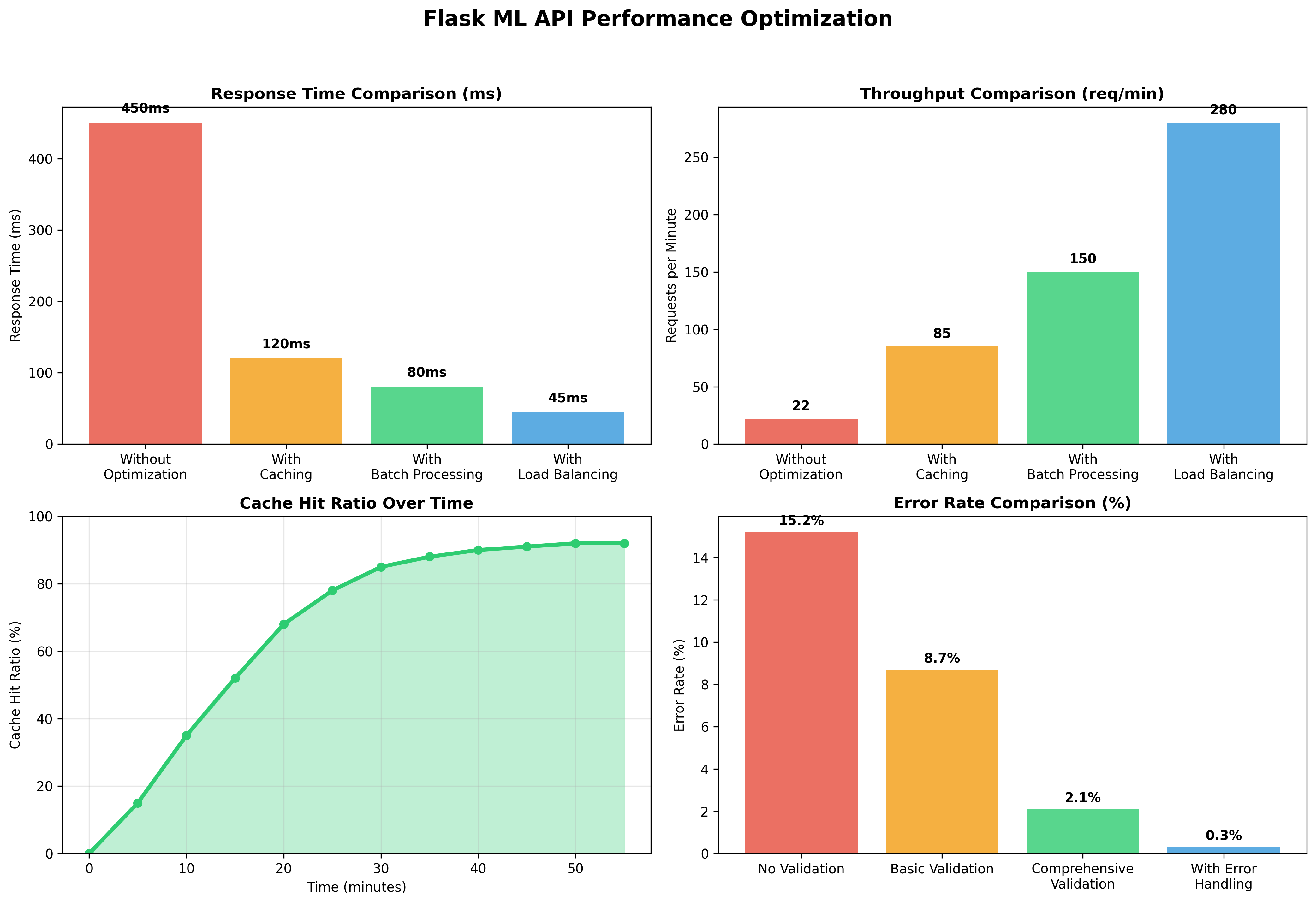 Figure 4: Performance optimization techniques for Flask ML APIs.
Figure 4: Performance optimization techniques for Flask ML APIs.
Security Considerations {#security}
API Security
# app/utils/security.py
from flask import request, jsonify
from functools import wraps
import jwt
import os
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import hashlib
import hmac
class APIKeyAuth:
"""Simple API key authentication"""
def __init__(self, api_keys: set):
self.api_keys = api_keys
def require_api_key(self, f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
api_key = request.headers.get('X-API-Key')
if not api_key or api_key not in self.api_keys:
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid or missing API key'}), 401
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
class RateLimiter:
"""Simple rate limiting"""
def __init__(self, max_requests: int = 100, window_seconds: int = 3600):
self.max_requests = max_requests
self.window_seconds = window_seconds
self.requests = {} # {ip: [timestamps]}
def is_allowed(self, identifier: str) -> bool:
"""Check if request is allowed"""
now = datetime.now()
cutoff = now - timedelta(seconds=self.window_seconds)
# Clean old requests
if identifier in self.requests:
self.requests[identifier] = [
timestamp for timestamp in self.requests[identifier]
if timestamp > cutoff
]
else:
self.requests[identifier] = []
# Check limit
if len(self.requests[identifier]) >= self.max_requests:
return False
# Add current request
self.requests[identifier].append(now)
return True
class InputSanitizer:
"""Sanitize and validate inputs"""
@staticmethod
def sanitize_features(features: list) -> list:
"""Sanitize feature inputs"""
sanitized = []
for feature in features:
if isinstance(feature, (int, float)):
# Clamp extreme values
sanitized.append(max(-1000, min(1000, float(feature))))
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid feature type: {type(feature)}")
return sanitized
@staticmethod
def validate_request_size(data: dict, max_size_mb: float = 10) -> bool:
"""Validate request size"""
import sys
size_bytes = sys.getsizeof(str(data))
size_mb = size_bytes / (1024 * 1024)
return size_mb <= max_size_mb
# Initialize security components
api_keys = {os.getenv('API_KEY_1', 'demo_key_123'),
os.getenv('API_KEY_2', 'demo_key_456')}
auth = APIKeyAuth(api_keys)
rate_limiter = RateLimiter(max_requests=50, window_seconds=3600)
Testing ML APIs {#testing}
Comprehensive Test Suite
# tests/test_api.py
import pytest
import json
import numpy as np
from app import create_app
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
@pytest.fixture
def client():
"""Create test client"""
app = create_app()
app.config['TESTING'] = True
# Load model for testing
model_manager.load_model()
with app.test_client() as client:
yield client
@pytest.fixture
def sample_features():
"""Sample features for testing"""
return np.random.randn(20).tolist()
@pytest.fixture
def sample_batch():
"""Sample batch for testing"""
return np.random.randn(5, 20).tolist()
class TestHealthEndpoint:
"""Test health check endpoint"""
def test_health_check(self, client):
response = client.get('/api/health')
assert response.status_code == 200
data = json.loads(response.data)
assert data['status'] == 'healthy'
assert 'model_loaded' in data
assert 'timestamp' in data
class TestPredictionEndpoints:
"""Test prediction endpoints"""
def test_single_prediction_success(self, client, sample_features):
response = client.post('/api/predict',
json={'features': sample_features},
content_type='application/json')
assert response.status_code == 200
data = json.loads(response.data)
assert data['success'] is True
assert 'result' in data
assert 'prediction' in data['result']
assert 'confidence' in data['result']
def test_single_prediction_invalid_input(self, client):
# Test with wrong number of features
response = client.post('/api/predict',
json={'features': [1, 2, 3]}, # Only 3 features
content_type='application/json')
assert response.status_code == 400
data = json.loads(response.data)
assert 'error' in data
def test_batch_prediction_success(self, client, sample_batch):
response = client.post('/api/predict/batch',
json={'samples': sample_batch},
content_type='application/json')
assert response.status_code == 200
data = json.loads(response.data)
assert data['success'] is True
assert len(data['results']) == 5
def test_missing_json_data(self, client):
response = client.post('/api/predict')
assert response.status_code == 400
data = json.loads(response.data)
assert 'No JSON data provided' in data['error']
class TestModelInfoEndpoint:
"""Test model information endpoint"""
def test_model_info(self, client):
response = client.get('/api/model/info')
assert response.status_code == 200
data = json.loads(response.data)
assert 'model_type' in data
assert 'n_features' in data
assert 'n_classes' in data
class TestErrorHandling:
"""Test error handling"""
def test_invalid_json(self, client):
response = client.post('/api/predict',
data='invalid json',
content_type='application/json')
assert response.status_code == 400
def test_nan_features(self, client):
features = [float('nan')] * 20
response = client.post('/api/predict',
json={'features': features},
content_type='application/json')
assert response.status_code == 400
# Performance tests
class TestPerformance:
"""Test API performance"""
def test_response_time(self, client, sample_features):
import time
start_time = time.time()
response = client.post('/api/predict',
json={'features': sample_features},
content_type='application/json')
end_time = time.time()
assert response.status_code == 200
assert (end_time - start_time) < 1.0 # Should respond within 1 second
def test_concurrent_requests(self, client, sample_features):
import threading
import time
results = []
def make_request():
response = client.post('/api/predict',
json={'features': sample_features},
content_type='application/json')
results.append(response.status_code)
# Create 10 concurrent threads
threads = []
for _ in range(10):
thread = threading.Thread(target=make_request)
threads.append(thread)
# Start all threads
for thread in threads:
thread.start()
# Wait for all threads to complete
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
# All requests should succeed
assert all(status == 200 for status in results)
assert len(results) == 10
Complete Project Example {#complete-example}
Let's create a complete real-world example: a sentiment analysis API.
Sentiment Analysis Model
# examples/sentiment_analysis/train_sentiment_model.py
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
import joblib
import re
import string
class TextPreprocessor:
"""Text preprocessing utilities"""
@staticmethod
def clean_text(text: str) -> str:
"""Clean and normalize text"""
# Convert to lowercase
text = text.lower()
# Remove URLs
text = re.sub(r'http\S+', '', text)
# Remove mentions and hashtags
text = re.sub(r'@\w+|#\w+', '', text)
# Remove punctuation
text = text.translate(str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation))
# Remove extra whitespace
text = ' '.join(text.split())
return text
def create_sample_data():
"""Create sample sentiment data"""
positive_texts = [
"I love this product, it's amazing!",
"Great service and excellent quality",
"Wonderful experience, highly recommend",
"Fantastic product, exceeded expectations",
"Love it! Will definitely buy again"
] * 100
negative_texts = [
"Terrible product, waste of money",
"Poor quality and bad service",
"Disappointed with the purchase",
"Not worth the price at all",
"Worst experience ever"
] * 100
neutral_texts = [
"The product is okay, nothing special",
"Average quality for the price",
"It's fine, does what it's supposed to do",
"Not bad, not great either",
"Standard product, meets basic needs"
] * 100
texts = positive_texts + negative_texts + neutral_texts
labels = [1] * 500 + [0] * 500 + [2] * 500 # 1: positive, 0: negative, 2: neutral
return texts, labels
def train_sentiment_model():
"""Train sentiment analysis model"""
# Create sample data (replace with real dataset)
texts, labels = create_sample_data()
# Split data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
texts, labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=labels
)
# Create preprocessing + model pipeline
pipeline = Pipeline([
('tfidf', TfidfVectorizer(
max_features=5000,
ngram_range=(1, 2),
stop_words='english'
)),
('classifier', LogisticRegression(
random_state=42,
max_iter=1000
))
])
# Train model
pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluate
y_pred = pipeline.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Model Accuracy: {accuracy:.3f}")
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred,
target_names=['Negative', 'Positive', 'Neutral']))
# Save model
joblib.dump(pipeline, 'models/sentiment_model.pkl')
print("Sentiment model saved!")
return pipeline
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_sentiment_model()
Sentiment API
# examples/sentiment_analysis/sentiment_api.py
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import joblib
import numpy as np
from typing import Dict, Any
import re
import string
app = Flask(__name__)
class SentimentAnalyzer:
"""Sentiment analysis model wrapper"""
def __init__(self):
self.model = None
self.label_map = {0: 'negative', 1: 'positive', 2: 'neutral'}
self.model_loaded = False
def load_model(self, model_path: str = 'models/sentiment_model.pkl'):
"""Load trained sentiment model"""
try:
self.model = joblib.load(model_path)
self.model_loaded = True
print("Sentiment model loaded successfully!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading model: {e}")
self.model_loaded = False
def predict_sentiment(self, text: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Predict sentiment for text"""
if not self.model_loaded:
raise ValueError("Model not loaded")
# Get prediction and probabilities
prediction = self.model.predict([text])[0]
probabilities = self.model.predict_proba([text])[0]
return {
'text': text,
'sentiment': self.label_map[prediction],
'confidence': float(max(probabilities)),
'probabilities': {
'negative': float(probabilities[0]),
'positive': float(probabilities[1]),
'neutral': float(probabilities[2])
}
}
def analyze_batch(self, texts: list) -> list:
"""Analyze sentiment for multiple texts"""
if not self.model_loaded:
raise ValueError("Model not loaded")
predictions = self.model.predict(texts)
probabilities = self.model.predict_proba(texts)
results = []
for i, (text, pred, probs) in enumerate(zip(texts, predictions, probabilities)):
results.append({
'id': i,
'text': text,
'sentiment': self.label_map[pred],
'confidence': float(max(probs)),
'probabilities': {
'negative': float(probs[0]),
'positive': float(probs[1]),
'neutral': float(probs[2])
}
})
return results
# Initialize analyzer
analyzer = SentimentAnalyzer()
analyzer.load_model()
@app.route('/health', methods=['GET'])
def health():
return jsonify({
'status': 'healthy',
'model_loaded': analyzer.model_loaded
})
@app.route('/analyze', methods=['POST'])
def analyze_sentiment():
"""Analyze sentiment for single text"""
try:
data = request.get_json()
if not data or 'text' not in data:
return jsonify({'error': 'Text field required'}), 400
text = data['text'].strip()
if not text:
return jsonify({'error': 'Text cannot be empty'}), 400
result = analyzer.predict_sentiment(text)
return jsonify({'success': True, 'result': result})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 500
@app.route('/analyze/batch', methods=['POST'])
def analyze_batch():
"""Analyze sentiment for multiple texts"""
try:
data = request.get_json()
if not data or 'texts' not in data:
return jsonify({'error': 'texts field required'}), 400
texts = data['texts']
if not isinstance(texts, list) or len(texts) == 0:
return jsonify({'error': 'texts must be non-empty list'}), 400
if len(texts) > 100:
return jsonify({'error': 'Maximum 100 texts allowed'}), 400
results = analyzer.analyze_batch(texts)
return jsonify({
'success': True,
'results': results,
'count': len(results)
})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 500
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True, host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
Deployment Strategies {#deployment}
Docker Deployment
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
# Copy requirements and install dependencies
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Copy application code
COPY . .
# Create models directory
RUN mkdir -p models
# Expose port
EXPOSE 5000
# Set environment variables
ENV FLASK_APP=run.py
ENV FLASK_ENV=production
# Health check
HEALTHCHECK --interval=30s --timeout=10s --start-period=5s --retries=3 \
CMD curl -f http://localhost:5000/api/health || exit 1
# Run application
CMD ["gunicorn", "--bind", "0.0.0.0:5000", "--workers", "4", "--timeout", "120", "run:app"]
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3.8'
services:
flask-ml-api:
build: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
environment:
- FLASK_ENV=production
- API_KEY_1=your_secure_api_key_here
volumes:
- ./models:/app/models
- ./logs:/app/logs
restart: unless-stopped
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost:5000/api/health"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
start_period: 40s
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
depends_on:
- flask-ml-api
restart: unless-stopped
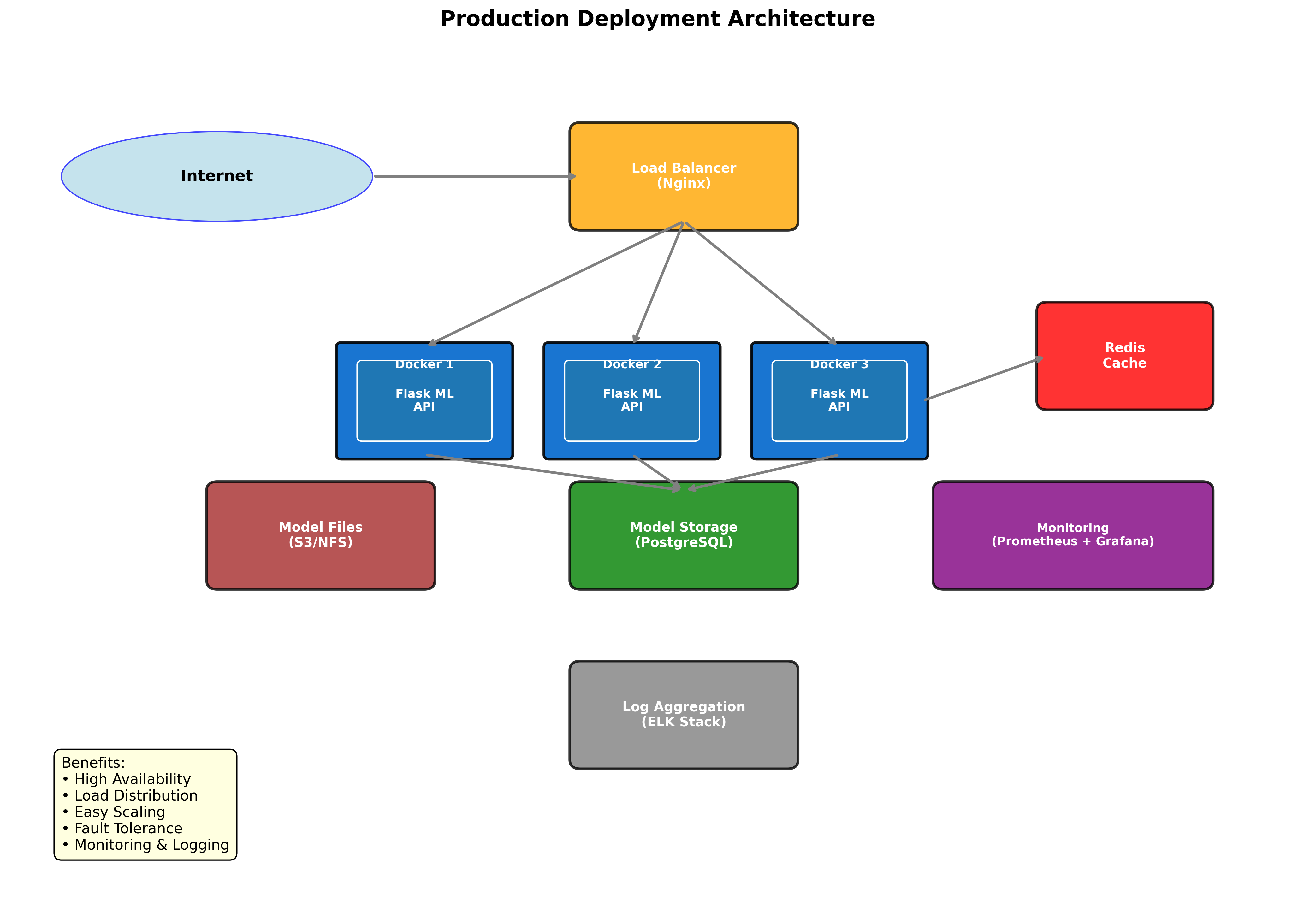 Figure 5: Production deployment architecture with Docker and load balancing.
Figure 5: Production deployment architecture with Docker and load balancing.
Monitoring and Logging {#monitoring}
Application Monitoring
# app/utils/monitoring.py
import logging
import time
from flask import request, g
from functools import wraps
import json
from datetime import datetime
class APILogger:
"""Comprehensive API logging"""
def __init__(self, app=None):
self.app = app
if app:
self.init_app(app)
def init_app(self, app):
"""Initialize logging for Flask app"""
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
handlers=[
logging.FileHandler('logs/api.log'),
logging.StreamHandler()
]
)
self.logger = logging.getLogger('flask_ml_api')
# Add request/response logging
app.before_request(self.before_request)
app.after_request(self.after_request)
def before_request(self):
"""Log incoming requests"""
g.start_time = time.time()
# Log request details
self.logger.info(f"Request: {request.method} {request.path}", extra={
'method': request.method,
'path': request.path,
'remote_addr': request.remote_addr,
'user_agent': request.headers.get('User-Agent'),
'content_length': request.content_length
})
def after_request(self, response):
"""Log response details"""
duration = time.time() - g.start_time
self.logger.info(f"Response: {response.status_code} ({duration:.3f}s)", extra={
'status_code': response.status_code,
'duration': duration,
'content_length': response.content_length
})
return response
def log_prediction(self, input_data, prediction, duration):
"""Log prediction details"""
self.logger.info("Prediction made", extra={
'prediction': prediction,
'duration': duration,
'input_size': len(str(input_data)),
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
def monitor_performance(f):
"""Decorator to monitor function performance"""
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
try:
result = f(*args, **kwargs)
duration = time.time() - start_time
# Log successful execution
logging.getLogger('performance').info(
f"{f.__name__} executed successfully in {duration:.3f}s"
)
return result
except Exception as e:
duration = time.time() - start_time
# Log error
logging.getLogger('performance').error(
f"{f.__name__} failed after {duration:.3f}s: {str(e)}"
)
raise
return decorated_function
Conclusion
Flask provides an excellent foundation for deploying machine learning models as web services. Its simplicity, flexibility, and extensive ecosystem make it ideal for everything from prototype APIs to production-scale deployments.
Key Takeaways
- Start Simple: Begin with basic model integration and gradually add features
- Validate Everything: Implement comprehensive input validation and error handling
- Think About Scale: Design for performance and scalability from the beginning
- Security First: Implement authentication, rate limiting, and input sanitization
- Monitor Everything: Add logging, metrics, and health checks
- Test Thoroughly: Create comprehensive test suites for reliability
Best Practices Summary
- Use proper project structure with separation of concerns
- Implement comprehensive error handling and validation
- Add caching for frequently requested predictions
- Use proper serialization for model persistence
- Implement security measures (API keys, rate limiting)
- Add monitoring and logging for production deployment
- Create thorough test suites
- Use containerization for consistent deployments
Next Steps
- Explore more advanced deployment options (Kubernetes, serverless)
- Implement more sophisticated caching strategies (Redis)
- Add real-time model monitoring and drift detection
- Integrate with ML pipeline orchestration tools
- Explore A/B testing for model versions
Flask's ecosystem continues to evolve, making it an excellent choice for machine learning deployment. Whether you're building a simple prototype or a complex production system, Flask provides the tools and flexibility needed to create robust ML APIs.
For more advanced topics in machine learning and web development, check out our posts on Bayesian Methods in Machine Learning and Gaussian Processes Explained.
Related Posts
More content from the Web Development category and similar topics
Master the art of building production-ready machine learning APIs with FastAPI. From basic model serving to advanced async processing and containerized deployment.
Shared topics:
Explore the fundamental principles of Bayesian machine learning, from basic probability theory to advanced applications in modern AI systems.
Shared topics:
Learn the fundamentals of Functional Data Analysis and how to implement key techniques using R.