FastAPI and Machine Learning Integration: A Complete Production Guide
FastAPI and Machine Learning Integration: A Complete Production Guide
FastAPI has revolutionized the way we build APIs in Python, especially for machine learning applications. With its async capabilities, automatic OpenAPI documentation, and high performance, FastAPI is the perfect choice for serving ML models at scale. This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about integrating machine learning models with FastAPI.

Why FastAPI for Machine Learning?
FastAPI offers several advantages for ML applications:
- High Performance: Built on Starlette and Pydantic, offering performance comparable to Node.js
- Async Support: Handle multiple requests concurrently without blocking
- Automatic Documentation: Interactive API docs with Swagger UI and ReDoc
- Type Safety: Built-in data validation and serialization with Python type hints
- Modern Python: Full support for Python 3.8+ features including async/await
1. Setting Up FastAPI for ML Integration
Project Structure
Let's start with a well-organized project structure:
fastapi-ml-project/
├── app/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── main.py
│ ├── models/
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── ml_models.py
│ │ └── schemas.py
│ ├── api/
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── endpoints/
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ ├── predict.py
│ │ │ └── health.py
│ │ └── dependencies.py
│ ├── core/
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── config.py
│ │ └── security.py
│ └── utils/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── preprocessing.py
├── models/
│ ├── sentiment_model.pkl
│ └── vectorizer.pkl
├── tests/
├── requirements.txt
├── Dockerfile
└── docker-compose.yml
Installation and Dependencies
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv fastapi-ml-env
source fastapi-ml-env/bin/activate # On Windows: fastapi-ml-env\Scripts\activate
# Install dependencies
pip install fastapi uvicorn scikit-learn pandas numpy pydantic python-multipart
pip install redis celery aioredis prometheus-client
Create requirements.txt:
fastapi==0.104.1
uvicorn[standard]==0.24.0
scikit-learn==1.3.2
pandas==2.1.4
numpy==1.25.2
pydantic==2.5.0
python-multipart==0.0.6
aioredis==2.0.1
celery==5.3.4
prometheus-client==0.19.0
python-jose[cryptography]==3.3.0
bcrypt==4.1.2
2. Basic ML Model Integration
Creating Pydantic Models
First, let's define our data models using Pydantic:
# app/models/schemas.py
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field, validator
from typing import List, Optional, Dict, Any
from enum import Enum
class PredictionRequest(BaseModel):
text: str = Field(..., min_length=1, max_length=1000, description="Text to analyze")
model_version: Optional[str] = Field("v1", description="Model version to use")
@validator('text')
def validate_text(cls, v):
if not v.strip():
raise ValueError('Text cannot be empty or whitespace only')
return v.strip()
class PredictionResponse(BaseModel):
prediction: str = Field(..., description="Predicted class")
confidence: float = Field(..., ge=0.0, le=1.0, description="Prediction confidence")
model_version: str = Field(..., description="Model version used")
processing_time: float = Field(..., description="Processing time in seconds")
class BatchPredictionRequest(BaseModel):
texts: List[str] = Field(..., min_items=1, max_items=100)
model_version: Optional[str] = "v1"
class BatchPredictionResponse(BaseModel):
predictions: List[PredictionResponse]
batch_size: int
total_processing_time: float
class ModelInfo(BaseModel):
name: str
version: str
accuracy: float
training_date: str
features: List[str]
class HealthResponse(BaseModel):
status: str
timestamp: str
version: str
models_loaded: Dict[str, bool]
ML Model Manager
Create a model manager to handle loading and serving models:
# app/models/ml_models.py
import pickle
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Tuple
import asyncio
import aiofiles
from datetime import datetime
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class MLModelManager:
def __init__(self):
self.models: Dict[str, Any] = {}
self.vectorizers: Dict[str, Any] = {}
self.model_info: Dict[str, Dict] = {}
async def load_model(self, model_name: str, model_path: str, vectorizer_path: str = None):
"""Load ML model asynchronously"""
try:
# Load model
async with aiofiles.open(model_path, 'rb') as f:
model_data = await f.read()
self.models[model_name] = pickle.loads(model_data)
# Load vectorizer if provided
if vectorizer_path:
async with aiofiles.open(vectorizer_path, 'rb') as f:
vectorizer_data = await f.read()
self.vectorizers[model_name] = pickle.loads(vectorizer_data)
# Store model info
self.model_info[model_name] = {
'loaded_at': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'model_path': model_path,
'vectorizer_path': vectorizer_path
}
logger.info(f"Model {model_name} loaded successfully")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error loading model {model_name}: {str(e)}")
raise
async def predict(self, model_name: str, text: str) -> Tuple[str, float]:
"""Make prediction asynchronously"""
if model_name not in self.models:
raise ValueError(f"Model {model_name} not loaded")
try:
# Preprocess text
if model_name in self.vectorizers:
features = self.vectorizers[model_name].transform([text])
else:
features = np.array([[len(text), text.count(' ')]]) # Simple features
# Make prediction
model = self.models[model_name]
prediction = model.predict(features)[0]
# Get confidence if available
if hasattr(model, 'predict_proba'):
probabilities = model.predict_proba(features)[0]
confidence = float(np.max(probabilities))
else:
confidence = 0.85 # Default confidence
return str(prediction), confidence
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error making prediction: {str(e)}")
raise
async def batch_predict(self, model_name: str, texts: List[str]) -> List[Tuple[str, float]]:
"""Make batch predictions asynchronously"""
if model_name not in self.models:
raise ValueError(f"Model {model_name} not loaded")
try:
# Preprocess texts
if model_name in self.vectorizers:
features = self.vectorizers[model_name].transform(texts)
else:
features = np.array([[len(text), text.count(' ')] for text in texts])
# Make predictions
model = self.models[model_name]
predictions = model.predict(features)
# Get confidences
if hasattr(model, 'predict_proba'):
probabilities = model.predict_proba(features)
confidences = np.max(probabilities, axis=1)
else:
confidences = np.full(len(predictions), 0.85)
return [(str(pred), float(conf)) for pred, conf in zip(predictions, confidences)]
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error making batch predictions: {str(e)}")
raise
def get_model_info(self, model_name: str) -> Dict:
"""Get model information"""
if model_name not in self.models:
raise ValueError(f"Model {model_name} not loaded")
return self.model_info.get(model_name, {})
def list_models(self) -> List[str]:
"""List all loaded models"""
return list(self.models.keys())
# Global model manager instance
model_manager = MLModelManager()
3. FastAPI Application Structure
Main Application
# app/main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Depends, BackgroundTasks
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
from fastapi.middleware.gzip import GZipMiddleware
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
import time
import logging
from pathlib import Path
from app.api.endpoints import predict, health
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
from app.core.config import Settings
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
settings = Settings()
@asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app: FastAPI):
# Startup
logger.info("Starting FastAPI ML application...")
# Load models
models_dir = Path("models")
if models_dir.exists():
await model_manager.load_model(
"sentiment_v1",
str(models_dir / "sentiment_model.pkl"),
str(models_dir / "vectorizer.pkl")
)
logger.info("Models loaded successfully")
yield
# Shutdown
logger.info("Shutting down FastAPI ML application...")
app = FastAPI(
title="FastAPI ML Integration",
description="Production-ready ML API with FastAPI",
version="1.0.0",
docs_url="/docs",
redoc_url="/redoc",
lifespan=lifespan
)
# Middleware
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["*"], # Configure appropriately for production
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)
app.add_middleware(GZipMiddleware, minimum_size=1000)
# Custom middleware for request timing
@app.middleware("http")
async def add_process_time_header(request, call_next):
start_time = time.time()
response = await call_next(request)
process_time = time.time() - start_time
response.headers["X-Process-Time"] = str(process_time)
return response
# Include routers
app.include_router(health.router, prefix="/api", tags=["health"])
app.include_router(predict.router, prefix="/api", tags=["predictions"])
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {
"message": "FastAPI ML Integration API",
"version": "1.0.0",
"docs": "/docs",
"health": "/api/health"
}
Configuration Management
# app/core/config.py
from pydantic_settings import BaseSettings
from typing import List, Optional
class Settings(BaseSettings):
# API Settings
API_TITLE: str = "FastAPI ML Integration"
API_VERSION: str = "1.0.0"
DEBUG: bool = False
# Security
SECRET_KEY: str = "your-secret-key-here"
ALGORITHM: str = "HS256"
ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES: int = 30
# Model Settings
DEFAULT_MODEL: str = "sentiment_v1"
MAX_BATCH_SIZE: int = 100
MODEL_CACHE_TTL: int = 3600
# Redis Settings
REDIS_URL: str = "redis://localhost:6379"
CACHE_ENABLED: bool = True
# Rate Limiting
RATE_LIMIT_REQUESTS: int = 100
RATE_LIMIT_WINDOW: int = 60
# Monitoring
METRICS_ENABLED: bool = True
LOG_LEVEL: str = "INFO"
class Config:
env_file = ".env"
settings = Settings()
4. API Endpoints Implementation
Prediction Endpoints
# app/api/endpoints/predict.py
from fastapi import APIRouter, HTTPException, Depends, BackgroundTasks
from typing import List
import time
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime
from app.models.schemas import (
PredictionRequest, PredictionResponse,
BatchPredictionRequest, BatchPredictionResponse,
ModelInfo
)
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
from app.core.config import settings
router = APIRouter()
@router.post("/predict", response_model=PredictionResponse)
async def predict_single(request: PredictionRequest):
"""Make a single prediction"""
try:
start_time = time.time()
# Make prediction
prediction, confidence = await model_manager.predict(
request.model_version,
request.text
)
processing_time = time.time() - start_time
return PredictionResponse(
prediction=prediction,
confidence=confidence,
model_version=request.model_version,
processing_time=processing_time
)
except ValueError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail=str(e))
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Prediction failed: {str(e)}")
@router.post("/predict/batch", response_model=BatchPredictionResponse)
async def predict_batch(request: BatchPredictionRequest):
"""Make batch predictions"""
try:
if len(request.texts) > settings.MAX_BATCH_SIZE:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=400,
detail=f"Batch size exceeds maximum of {settings.MAX_BATCH_SIZE}"
)
start_time = time.time()
# Make batch predictions
results = await model_manager.batch_predict(
request.model_version,
request.texts
)
total_processing_time = time.time() - start_time
# Format responses
predictions = []
for i, (prediction, confidence) in enumerate(results):
predictions.append(PredictionResponse(
prediction=prediction,
confidence=confidence,
model_version=request.model_version,
processing_time=total_processing_time / len(request.texts)
))
return BatchPredictionResponse(
predictions=predictions,
batch_size=len(request.texts),
total_processing_time=total_processing_time
)
except ValueError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail=str(e))
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Batch prediction failed: {str(e)}")
@router.get("/models", response_model=List[str])
async def list_models():
"""List all available models"""
try:
return model_manager.list_models()
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Failed to list models: {str(e)}")
@router.get("/models/{model_name}/info", response_model=ModelInfo)
async def get_model_info(model_name: str):
"""Get information about a specific model"""
try:
info = model_manager.get_model_info(model_name)
return ModelInfo(
name=model_name,
version=info.get('version', 'v1'),
accuracy=info.get('accuracy', 0.85),
training_date=info.get('loaded_at', datetime.now().isoformat()),
features=info.get('features', ['text_features'])
)
except ValueError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail=str(e))
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Failed to get model info: {str(e)}")
@router.post("/models/{model_name}/reload")
async def reload_model(model_name: str, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
"""Reload a specific model"""
async def reload_task():
try:
# This would typically reload from a model registry or storage
await model_manager.load_model(
model_name,
f"models/{model_name}_model.pkl",
f"models/{model_name}_vectorizer.pkl"
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to reload model {model_name}: {str(e)}")
background_tasks.add_task(reload_task)
return {"message": f"Model {model_name} reload initiated"}
Health Check Endpoints
# app/api/endpoints/health.py
from fastapi import APIRouter, HTTPException
from datetime import datetime
import psutil
import asyncio
from app.models.schemas import HealthResponse
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
router = APIRouter()
@router.get("/health", response_model=HealthResponse)
async def health_check():
"""Comprehensive health check"""
try:
# Check model availability
models_loaded = {}
for model_name in model_manager.list_models():
try:
# Test prediction to ensure model is working
_, _ = await model_manager.predict(model_name, "test")
models_loaded[model_name] = True
except:
models_loaded[model_name] = False
return HealthResponse(
status="healthy" if all(models_loaded.values()) else "degraded",
timestamp=datetime.now().isoformat(),
version="1.0.0",
models_loaded=models_loaded
)
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Health check failed: {str(e)}")
@router.get("/health/detailed")
async def detailed_health_check():
"""Detailed system health check"""
try:
# System metrics
cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
memory = psutil.virtual_memory()
disk = psutil.disk_usage('/')
# Model status
models_status = {}
for model_name in model_manager.list_models():
info = model_manager.get_model_info(model_name)
models_status[model_name] = {
"loaded": True,
"loaded_at": info.get('loaded_at'),
"memory_usage": "N/A" # Would need to implement memory tracking
}
return {
"status": "healthy",
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"system": {
"cpu_percent": cpu_percent,
"memory_percent": memory.percent,
"memory_available": memory.available,
"disk_percent": (disk.used / disk.total) * 100
},
"models": models_status,
"uptime": "N/A" # Would need to track application start time
}
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Detailed health check failed: {str(e)}")
@router.get("/ready")
async def readiness_check():
"""Kubernetes readiness probe"""
try:
# Check if at least one model is loaded
models = model_manager.list_models()
if not models:
raise HTTPException(status_code=503, detail="No models loaded")
return {"status": "ready", "models_count": len(models)}
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=503, detail=f"Not ready: {str(e)}")
@router.get("/live")
async def liveness_check():
"""Kubernetes liveness probe"""
return {"status": "alive", "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()}
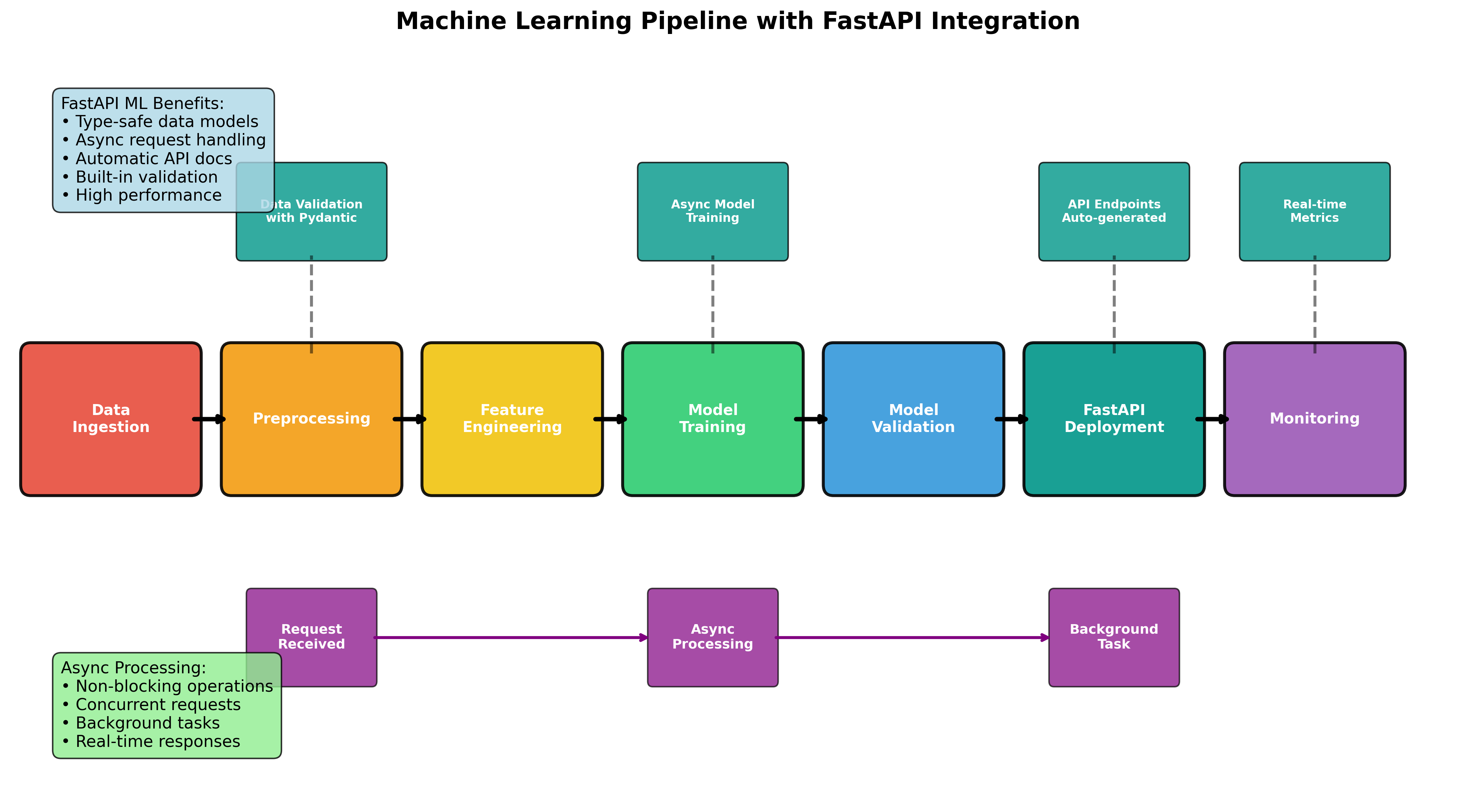
5. Advanced Features
Async Processing with Background Tasks
# app/api/endpoints/async_predict.py
from fastapi import APIRouter, BackgroundTasks, HTTPException
from typing import Dict, List
import uuid
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from app.models.schemas import PredictionRequest
router = APIRouter()
# In-memory storage for demo (use Redis in production)
task_results: Dict[str, Dict] = {}
@router.post("/predict/async")
async def async_predict(
request: PredictionRequest,
background_tasks: BackgroundTasks
):
"""Submit async prediction task"""
task_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
# Store initial task status
task_results[task_id] = {
"status": "pending",
"created_at": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"result": None,
"error": None
}
# Add background task
background_tasks.add_task(process_async_prediction, task_id, request)
return {
"task_id": task_id,
"status": "submitted",
"check_url": f"/api/predict/async/{task_id}"
}
async def process_async_prediction(task_id: str, request: PredictionRequest):
"""Process prediction in background"""
try:
task_results[task_id]["status"] = "processing"
# Simulate long-running task
await asyncio.sleep(2)
# Make prediction
from app.models.ml_models import model_manager
prediction, confidence = await model_manager.predict(
request.model_version,
request.text
)
# Store result
task_results[task_id].update({
"status": "completed",
"result": {
"prediction": prediction,
"confidence": confidence,
"model_version": request.model_version
},
"completed_at": datetime.now().isoformat()
})
except Exception as e:
task_results[task_id].update({
"status": "failed",
"error": str(e),
"failed_at": datetime.now().isoformat()
})
@router.get("/predict/async/{task_id}")
async def get_async_result(task_id: str):
"""Get async prediction result"""
if task_id not in task_results:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Task not found")
return task_results[task_id]
Caching with Redis
# app/utils/cache.py
import aioredis
import json
import hashlib
from typing import Optional, Any
from app.core.config import settings
class CacheManager:
def __init__(self):
self.redis: Optional[aioredis.Redis] = None
async def connect(self):
"""Connect to Redis"""
if settings.CACHE_ENABLED:
self.redis = aioredis.from_url(settings.REDIS_URL)
async def disconnect(self):
"""Disconnect from Redis"""
if self.redis:
await self.redis.close()
def _generate_key(self, prefix: str, data: str) -> str:
"""Generate cache key"""
hash_obj = hashlib.md5(data.encode())
return f"{prefix}:{hash_obj.hexdigest()}"
async def get_prediction(self, model_name: str, text: str) -> Optional[tuple]:
"""Get cached prediction"""
if not self.redis:
return None
key = self._generate_key(f"pred:{model_name}", text)
cached = await self.redis.get(key)
if cached:
result = json.loads(cached)
return result['prediction'], result['confidence']
return None
async def set_prediction(self, model_name: str, text: str, prediction: str, confidence: float):
"""Cache prediction result"""
if not self.redis:
return
key = self._generate_key(f"pred:{model_name}", text)
value = json.dumps({
'prediction': prediction,
'confidence': confidence,
'cached_at': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
await self.redis.setex(key, settings.MODEL_CACHE_TTL, value)
cache_manager = CacheManager()
6. Security and Authentication
JWT Authentication
# app/core/security.py
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Optional
from jose import JWTError, jwt
from passlib.context import CryptContext
from fastapi import HTTPException, status, Depends
from fastapi.security import HTTPBearer, HTTPAuthorizationCredentials
from app.core.config import settings
pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto")
security = HTTPBearer()
def create_access_token(data: dict, expires_delta: Optional[timedelta] = None):
"""Create JWT access token"""
to_encode = data.copy()
if expires_delta:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + expires_delta
else:
expire = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=settings.ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES)
to_encode.update({"exp": expire})
encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, settings.SECRET_KEY, algorithm=settings.ALGORITHM)
return encoded_jwt
def verify_token(credentials: HTTPAuthorizationCredentials = Depends(security)):
"""Verify JWT token"""
try:
payload = jwt.decode(credentials.credentials, settings.SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[settings.ALGORITHM])
username: str = payload.get("sub")
if username is None:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Could not validate credentials",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
return username
except JWTError:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
detail="Could not validate credentials",
headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
)
# Rate limiting decorator
from functools import wraps
import time
class RateLimiter:
def __init__(self):
self.requests = {}
def limit(self, max_requests: int = 100, window: int = 60):
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
now = time.time()
# Simple in-memory rate limiting (use Redis in production)
client_id = "default" # Should be based on IP or user
if client_id not in self.requests:
self.requests[client_id] = []
# Clean old requests
self.requests[client_id] = [
req_time for req_time in self.requests[client_id]
if now - req_time < window
]
# Check rate limit
if len(self.requests[client_id]) >= max_requests:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS,
detail="Rate limit exceeded"
)
# Add current request
self.requests[client_id].append(now)
return await func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return decorator
rate_limiter = RateLimiter()
7. Testing Strategy
Unit Tests
# tests/test_predict.py
import pytest
from fastapi.testclient import TestClient
from app.main import app
client = TestClient(app)
class TestPredictionEndpoints:
def test_single_prediction(self):
"""Test single prediction endpoint"""
response = client.post(
"/api/predict",
json={
"text": "I love this product!",
"model_version": "sentiment_v1"
}
)
assert response.status_code == 200
data = response.json()
assert "prediction" in data
assert "confidence" in data
assert data["model_version"] == "sentiment_v1"
assert 0 <= data["confidence"] <= 1
def test_batch_prediction(self):
"""Test batch prediction endpoint"""
response = client.post(
"/api/predict/batch",
json={
"texts": [
"Great product!",
"Terrible experience",
"Average quality"
],
"model_version": "sentiment_v1"
}
)
assert response.status_code == 200
data = response.json()
assert len(data["predictions"]) == 3
assert data["batch_size"] == 3
def test_invalid_input(self):
"""Test invalid input handling"""
response = client.post(
"/api/predict",
json={
"text": "", # Empty text
"model_version": "sentiment_v1"
}
)
assert response.status_code == 422 # Validation error
def test_model_info(self):
"""Test model info endpoint"""
response = client.get("/api/models/sentiment_v1/info")
assert response.status_code == 200
data = response.json()
assert data["name"] == "sentiment_v1"
assert "accuracy" in data
@pytest.mark.asyncio
async def test_async_prediction():
"""Test async prediction flow"""
# Submit async task
response = client.post(
"/api/predict/async",
json={
"text": "Test async prediction",
"model_version": "sentiment_v1"
}
)
assert response.status_code == 200
task_id = response.json()["task_id"]
# Check result (may need to wait/retry in real tests)
result_response = client.get(f"/api/predict/async/{task_id}")
assert result_response.status_code == 200
Load Testing
# tests/load_test.py
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import time
from statistics import mean, median
async def load_test_predictions(num_requests: int = 100, concurrent: int = 10):
"""Load test prediction endpoint"""
url = "http://localhost:8000/api/predict"
payload = {
"text": "This is a load test message",
"model_version": "sentiment_v1"
}
response_times = []
errors = 0
async def make_request(session):
start_time = time.time()
try:
async with session.post(url, json=payload) as response:
await response.json()
if response.status == 200:
response_times.append(time.time() - start_time)
else:
errors += 1
except Exception:
errors += 1
# Create semaphore for concurrency control
semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(concurrent)
async def bounded_request(session):
async with semaphore:
await make_request(session)
# Run load test
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
tasks = [bounded_request(session) for _ in range(num_requests)]
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# Print results
if response_times:
print(f"Requests: {len(response_times)}")
print(f"Errors: {errors}")
print(f"Mean response time: {mean(response_times):.3f}s")
print(f"Median response time: {median(response_times):.3f}s")
print(f"Min response time: {min(response_times):.3f}s")
print(f"Max response time: {max(response_times):.3f}s")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(load_test_predictions())
8. Docker Deployment
Dockerfile
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.11-slim
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Install system dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
gcc \
g++ \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Copy requirements and install Python dependencies
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Copy application code
COPY app/ ./app/
COPY models/ ./models/
# Create non-root user
RUN useradd --create-home --shell /bin/bash app && chown -R app:app /app
USER app
# Expose port
EXPOSE 8000
# Health check
HEALTHCHECK --interval=30s --timeout=10s --start-period=30s --retries=3 \
CMD curl -f http://localhost:8000/api/health || exit 1
# Start command
CMD ["uvicorn", "app.main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8000", "--workers", "4"]
Docker Compose
# docker-compose.yml
version: '3.8'
services:
fastapi-ml:
build: .
ports:
- "8000:8000"
environment:
- REDIS_URL=redis://redis:6379
- DEBUG=false
depends_on:
- redis
volumes:
- ./models:/app/models:ro
restart: unless-stopped
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost:8000/api/health"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
ports:
- "6379:6379"
command: redis-server --appendonly yes
volumes:
- redis_data:/data
restart: unless-stopped
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:ro
depends_on:
- fastapi-ml
restart: unless-stopped
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus
ports:
- "9090:9090"
volumes:
- ./prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml:ro
restart: unless-stopped
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin
volumes:
- grafana_data:/var/lib/grafana
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
redis_data:
grafana_data:
Nginx Configuration
# nginx.conf
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
upstream fastapi_backend {
server fastapi-ml:8000;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://fastapi_backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Timeout settings
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
}
# Health check endpoint
location /health {
proxy_pass http://fastapi_backend/api/health;
}
}
}
9. Monitoring and Observability
Prometheus Metrics
# app/utils/metrics.py
from prometheus_client import Counter, Histogram, Gauge, generate_latest
import time
from functools import wraps
# Metrics
REQUEST_COUNT = Counter('fastapi_requests_total', 'Total requests', ['method', 'endpoint', 'status'])
REQUEST_DURATION = Histogram('fastapi_request_duration_seconds', 'Request duration')
PREDICTION_COUNT = Counter('ml_predictions_total', 'Total predictions', ['model', 'status'])
MODEL_LOAD_TIME = Histogram('ml_model_load_seconds', 'Model loading time')
ACTIVE_MODELS = Gauge('ml_models_loaded', 'Number of loaded models')
def track_requests(func):
"""Decorator to track request metrics"""
@wraps(func)
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
try:
result = await func(*args, **kwargs)
REQUEST_COUNT.labels(method='POST', endpoint=func.__name__, status='success').inc()
return result
except Exception as e:
REQUEST_COUNT.labels(method='POST', endpoint=func.__name__, status='error').inc()
raise
finally:
REQUEST_DURATION.observe(time.time() - start_time)
return wrapper
def track_predictions(func):
"""Decorator to track prediction metrics"""
@wraps(func)
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
result = await func(*args, **kwargs)
PREDICTION_COUNT.labels(model='default', status='success').inc()
return result
except Exception as e:
PREDICTION_COUNT.labels(model='default', status='error').inc()
raise
return wrapper
Structured Logging
# app/utils/logging.py
import logging
import json
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, Any
class StructuredFormatter(logging.Formatter):
"""Custom formatter for structured logging"""
def format(self, record):
log_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'level': record.levelname,
'logger': record.name,
'message': record.getMessage(),
'module': record.module,
'function': record.funcName,
'line': record.lineno
}
# Add extra fields if present
if hasattr(record, 'extra_fields'):
log_entry.update(record.extra_fields)
return json.dumps(log_entry)
def setup_logging():
"""Setup structured logging"""
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
handler = logging.StreamHandler()
handler.setFormatter(StructuredFormatter())
logger.addHandler(handler)
return logger
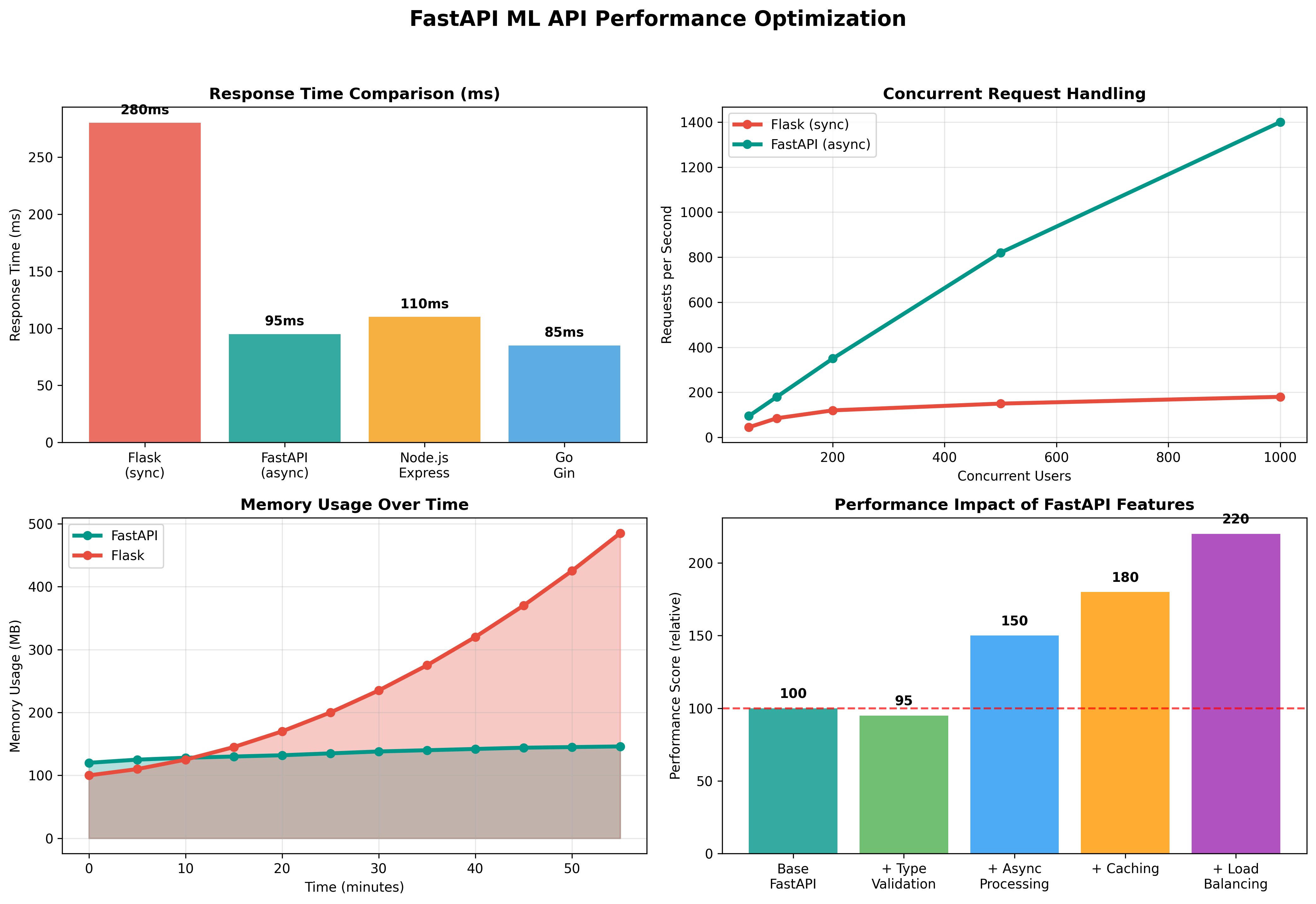
10. Performance Optimization
Connection Pooling and Async Optimization
# app/utils/optimization.py
import asyncio
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from typing import List, Any
import numpy as np
class AsyncMLProcessor:
def __init__(self, max_workers: int = 4):
self.executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers)
async def async_predict(self, model, features):
"""Run CPU-intensive prediction in thread pool"""
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
return await loop.run_in_executor(
self.executor,
model.predict,
features
)
async def batch_process(self, model, batch_features: List[np.ndarray], batch_size: int = 32):
"""Process large batches efficiently"""
results = []
# Process in chunks to avoid memory issues
for i in range(0, len(batch_features), batch_size):
chunk = batch_features[i:i + batch_size]
chunk_features = np.vstack(chunk)
# Process chunk asynchronously
chunk_result = await self.async_predict(model, chunk_features)
results.extend(chunk_result)
return results
async def parallel_model_inference(self, models: dict, features):
"""Run inference on multiple models in parallel"""
tasks = []
for model_name, model in models.items():
task = self.async_predict(model, features)
tasks.append((model_name, task))
results = {}
for model_name, task in tasks:
results[model_name] = await task
return results
# Global processor instance
ml_processor = AsyncMLProcessor()
Response Caching and Compression
# app/middleware/caching.py
from fastapi import Request, Response
from typing import Dict, Optional
import hashlib
import json
import gzip
class ResponseCache:
def __init__(self, max_size: int = 1000):
self.cache: Dict[str, bytes] = {}
self.max_size = max_size
def _generate_key(self, request: Request) -> str:
"""Generate cache key from request"""
key_data = f"{request.method}:{request.url}:{request.headers.get('content-type', '')}"
return hashlib.md5(key_data.encode()).hexdigest()
def get(self, key: str) -> Optional[bytes]:
"""Get cached response"""
return self.cache.get(key)
def set(self, key: str, response: bytes):
"""Cache response"""
if len(self.cache) >= self.max_size:
# Simple LRU: remove oldest entry
oldest_key = next(iter(self.cache))
del self.cache[oldest_key]
self.cache[key] = response
# Response compression middleware
async def gzip_response(request: Request, call_next):
"""Compress responses"""
response = await call_next(request)
# Only compress if client accepts gzip and response is large enough
accept_encoding = request.headers.get('accept-encoding', '')
if 'gzip' in accept_encoding and hasattr(response, 'body'):
body = response.body
if len(body) > 1000: # Only compress responses > 1KB
compressed_body = gzip.compress(body)
response.headers['content-encoding'] = 'gzip'
response.headers['content-length'] = str(len(compressed_body))
# Update response body (implementation depends on FastAPI version)
return response
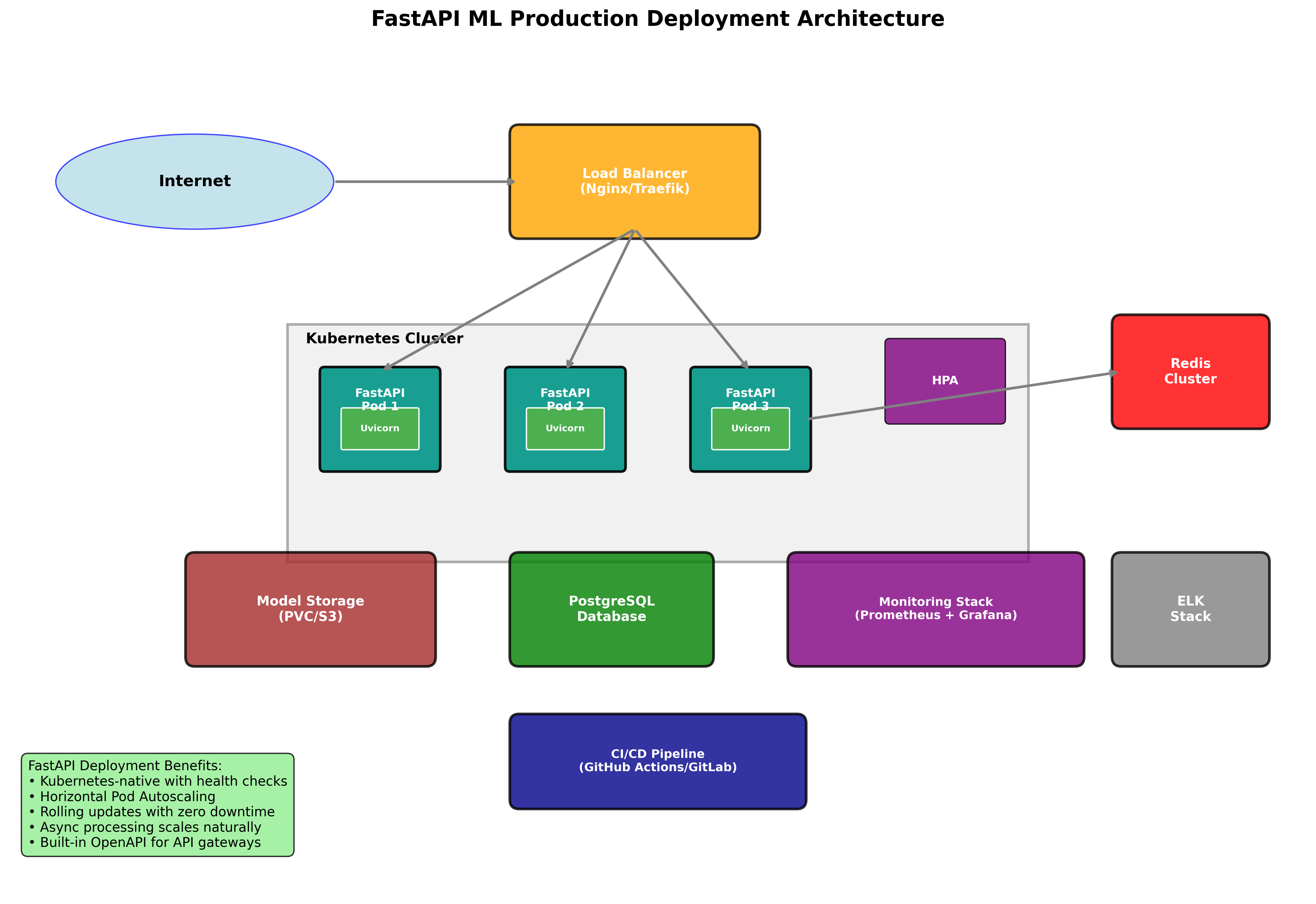
11. Production Deployment Strategies
Kubernetes Deployment
# k8s/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: fastapi-ml
labels:
app: fastapi-ml
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: fastapi-ml
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: fastapi-ml
spec:
containers:
- name: fastapi-ml
image: your-registry/fastapi-ml:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
env:
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis://redis-service:6379"
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "250m"
limits:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "500m"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/live
port: 8000
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/ready
port: 8000
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
volumeMounts:
- name: model-storage
mountPath: /app/models
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: model-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: model-pvc
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fastapi-ml-service
spec:
selector:
app: fastapi-ml
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8000
type: LoadBalancer
---
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: fastapi-ml-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: fastapi-ml
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 80
CI/CD Pipeline
# .github/workflows/deploy.yml
name: Deploy FastAPI ML
on:
push:
branches: [main]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: '3.11'
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install pytest pytest-asyncio
- name: Run tests
run: pytest tests/ -v
- name: Run security checks
run: |
pip install bandit safety
bandit -r app/
safety check
build:
needs: test
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Build Docker image
run: |
docker build -t fastapi-ml:${{ github.sha }} .
docker tag fastapi-ml:${{ github.sha }} fastapi-ml:latest
- name: Push to registry
run: |
# Push to your container registry
echo "Push to registry here"
deploy:
needs: build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Deploy to production
run: |
# Deploy using your preferred method (kubectl, helm, etc.)
echo "Deploy to production here"
12. Best Practices and Production Considerations
Model Versioning and A/B Testing
# app/models/model_registry.py
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
import json
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
class ModelStatus(Enum):
ACTIVE = "active"
STAGING = "staging"
DEPRECATED = "deprecated"
@dataclass
class ModelVersion:
name: str
version: str
path: str
status: ModelStatus
accuracy: float
created_at: str
traffic_percentage: float = 0.0
class ModelRegistry:
def __init__(self):
self.models: Dict[str, List[ModelVersion]] = {}
self.routing_config: Dict[str, Dict] = {}
def register_model(self, model_version: ModelVersion):
"""Register a new model version"""
if model_version.name not in self.models:
self.models[model_version.name] = []
self.models[model_version.name].append(model_version)
def get_model_for_request(self, model_name: str, request_id: str = None) -> ModelVersion:
"""Get model version based on A/B testing rules"""
if model_name not in self.models:
raise ValueError(f"Model {model_name} not found")
versions = self.models[model_name]
active_versions = [v for v in versions if v.status == ModelStatus.ACTIVE]
if not active_versions:
raise ValueError(f"No active versions for model {model_name}")
# Simple A/B testing based on request hash
if request_id and len(active_versions) > 1:
hash_val = hash(request_id) % 100
cumulative = 0
for version in active_versions:
cumulative += version.traffic_percentage
if hash_val < cumulative:
return version
# Return primary version (highest traffic percentage)
return max(active_versions, key=lambda v: v.traffic_percentage)
def update_traffic_split(self, model_name: str, version_splits: Dict[str, float]):
"""Update traffic split between model versions"""
if model_name not in self.models:
raise ValueError(f"Model {model_name} not found")
total_traffic = sum(version_splits.values())
if abs(total_traffic - 100.0) > 0.01:
raise ValueError("Traffic percentages must sum to 100")
for version in self.models[model_name]:
if version.version in version_splits:
version.traffic_percentage = version_splits[version.version]
Error Handling and Circuit Breaker
# app/utils/circuit_breaker.py
import asyncio
import time
from enum import Enum
from typing import Callable, Any
from functools import wraps
class CircuitState(Enum):
CLOSED = "closed"
OPEN = "open"
HALF_OPEN = "half_open"
class CircuitBreaker:
def __init__(
self,
failure_threshold: int = 5,
recovery_timeout: int = 60,
expected_exception: Exception = Exception
):
self.failure_threshold = failure_threshold
self.recovery_timeout = recovery_timeout
self.expected_exception = expected_exception
self.failure_count = 0
self.last_failure_time = None
self.state = CircuitState.CLOSED
def __call__(self, func: Callable) -> Callable:
@wraps(func)
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
if self.state == CircuitState.OPEN:
if self._should_attempt_reset():
self.state = CircuitState.HALF_OPEN
else:
raise Exception("Circuit breaker is OPEN")
try:
result = await func(*args, **kwargs)
self._on_success()
return result
except self.expected_exception as e:
self._on_failure()
raise e
return wrapper
def _should_attempt_reset(self) -> bool:
return (
self.last_failure_time and
time.time() - self.last_failure_time >= self.recovery_timeout
)
def _on_success(self):
self.failure_count = 0
self.state = CircuitState.CLOSED
def _on_failure(self):
self.failure_count += 1
self.last_failure_time = time.time()
if self.failure_count >= self.failure_threshold:
self.state = CircuitState.OPEN
# Usage example
@CircuitBreaker(failure_threshold=3, recovery_timeout=30)
async def ml_prediction_with_circuit_breaker(model, features):
"""ML prediction with circuit breaker protection"""
return await model.predict(features)
13. Monitoring and Alerting
Custom Metrics and Alerts
# app/utils/monitoring.py
import asyncio
import time
from typing import Dict, List
from dataclasses import dataclass
from prometheus_client import CollectorRegistry, Counter, Histogram, Gauge
@dataclass
class Alert:
name: str
condition: str
threshold: float
message: str
severity: str
class MonitoringSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.registry = CollectorRegistry()
self.metrics = {
'prediction_latency': Histogram(
'ml_prediction_latency_seconds',
'ML prediction latency',
registry=self.registry
),
'model_accuracy': Gauge(
'ml_model_accuracy',
'Model accuracy score',
['model_name'],
registry=self.registry
),
'error_rate': Counter(
'ml_prediction_errors_total',
'ML prediction errors',
['model_name', 'error_type'],
registry=self.registry
)
}
self.alerts: List[Alert] = [
Alert(
name="high_latency",
condition="prediction_latency > 2.0",
threshold=2.0,
message="ML prediction latency is high",
severity="warning"
),
Alert(
name="low_accuracy",
condition="model_accuracy < 0.8",
threshold=0.8,
message="Model accuracy has dropped",
severity="critical"
)
]
async def check_alerts(self):
"""Check alert conditions and trigger notifications"""
# This would integrate with alerting systems like PagerDuty, Slack, etc.
pass
def record_prediction_metrics(self, model_name: str, latency: float, success: bool):
"""Record prediction metrics"""
self.metrics['prediction_latency'].observe(latency)
if not success:
self.metrics['error_rate'].labels(
model_name=model_name,
error_type="prediction_failed"
).inc()
monitoring = MonitoringSystem()
14. Conclusion
FastAPI provides an excellent foundation for building production-ready machine learning APIs. Its async capabilities, automatic documentation, and robust ecosystem make it ideal for ML applications that need to handle high throughput and provide reliable service.
Key Takeaways
- Performance: FastAPI's async nature allows handling thousands of concurrent requests
- Developer Experience: Automatic API documentation and type safety reduce development time
- Production Ready: Built-in support for validation, security, and monitoring
- Scalability: Easy to containerize and deploy with horizontal scaling
- Ecosystem: Rich ecosystem of extensions and integrations
Next Steps
- Model Management: Implement MLOps practices with model versioning and automated deployment
- Advanced Monitoring: Set up comprehensive observability with distributed tracing
- Security Hardening: Implement advanced security measures for production environments
- Performance Optimization: Fine-tune for your specific use case and traffic patterns
Resources
FastAPI and machine learning make a powerful combination. With the patterns and practices outlined in this guide, you're well-equipped to build scalable, maintainable ML APIs that can handle production workloads effectively.
This guide provides a comprehensive foundation for FastAPI ML integration. Remember to adapt the examples to your specific use case and always test thoroughly in a staging environment before deploying to production.
Related Posts
More content from the Machine Learning category and similar topics
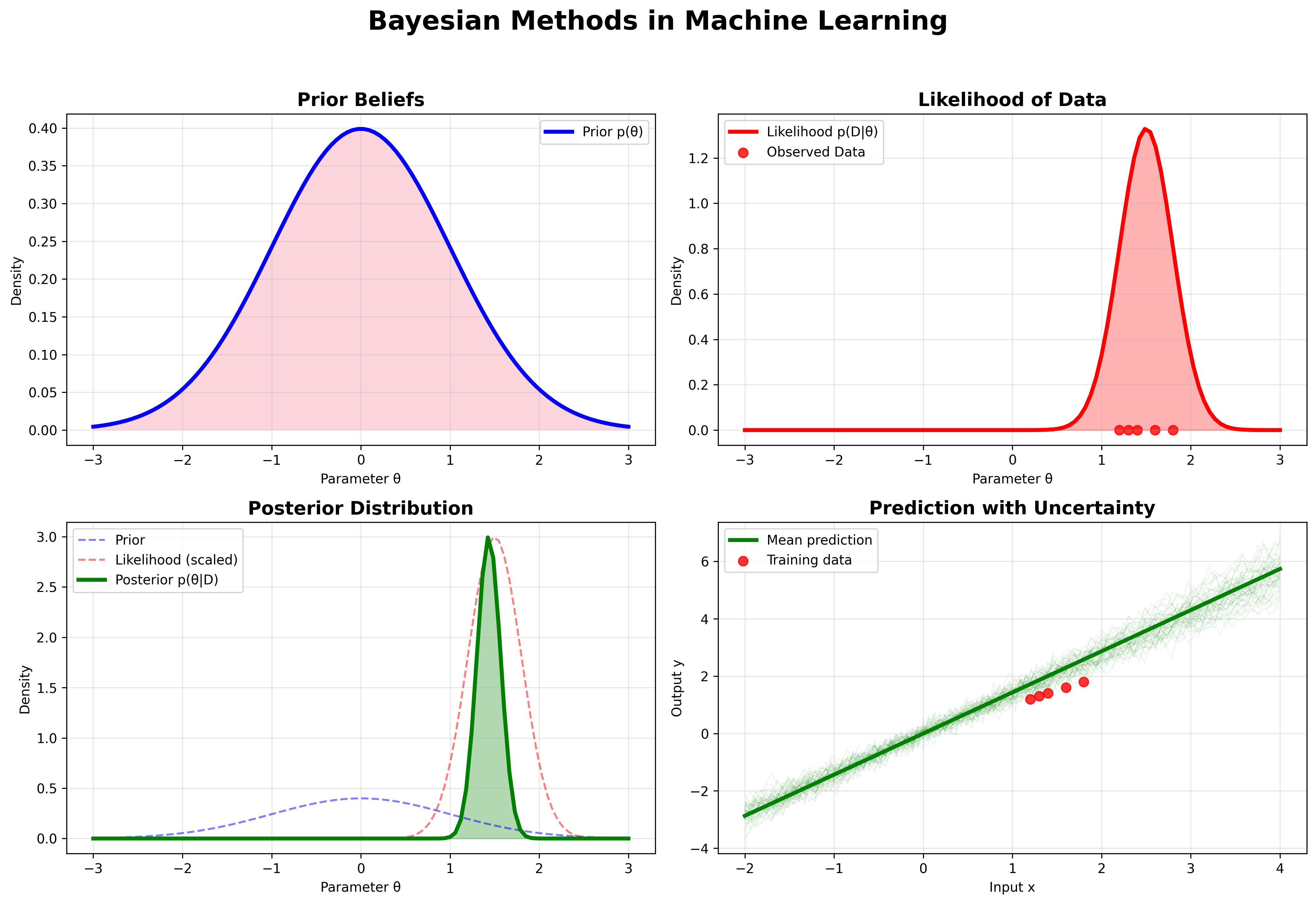
Explore the fundamental principles of Bayesian machine learning, from basic probability theory to advanced applications in modern AI systems.
Shared topics:
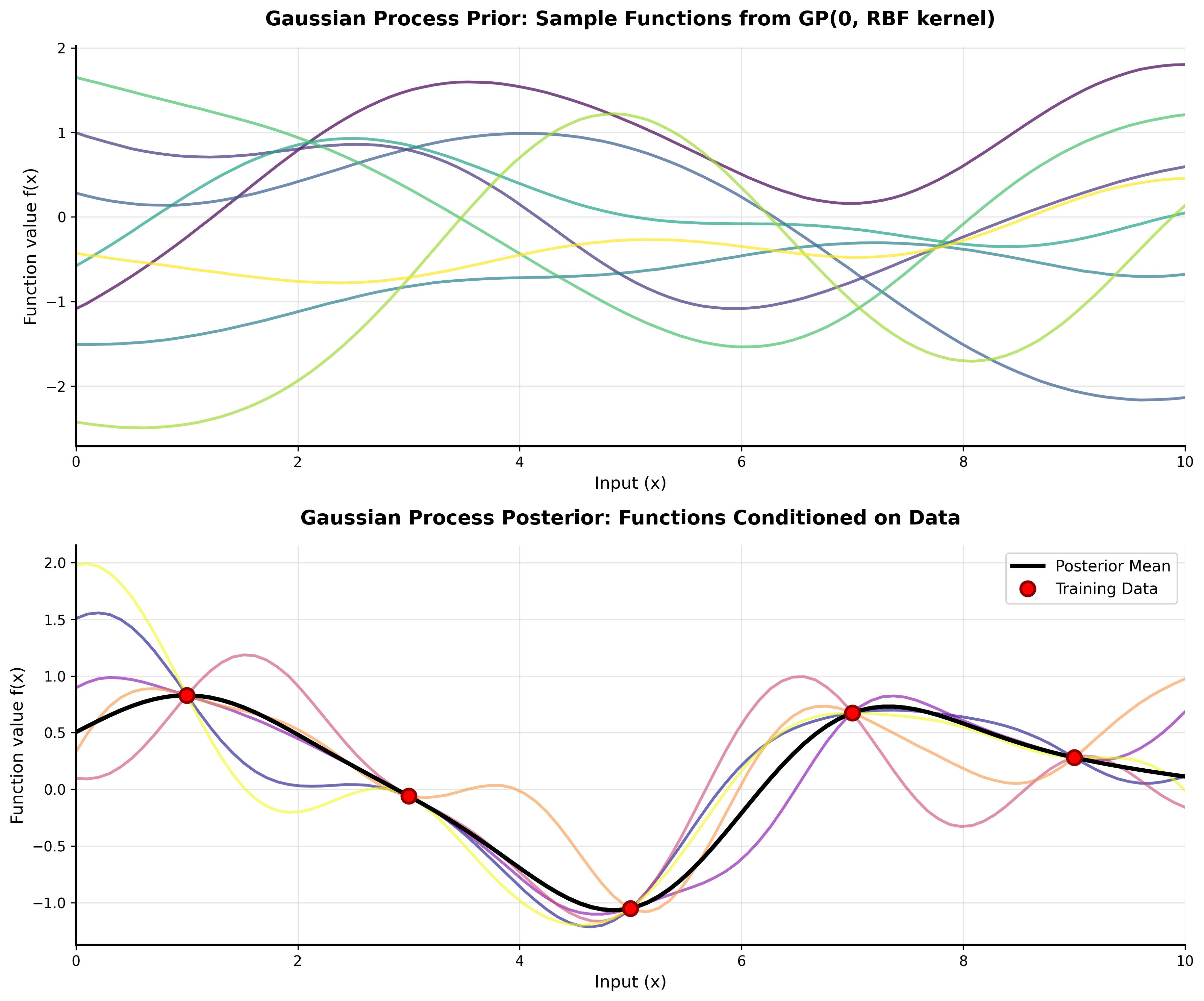
A comprehensive tutorial on understanding Gaussian Processes with interactive visualizations and practical examples.
A comprehensive tutorial on understanding Gaussian Processes with interactive visualizations and practical examples.